Greening the Grid: How We Helped Reducing The Carbon Footprint with Sustainable Software Practices
Discover how re:cinq optimised a company's infrastructure to halve its carbon emissions using sustainable IT practices.

This case study explores how re:cinq, a company specialising in sustainable software practices, helped another company optimise their software setup to reduce carbon emissions. Both companies are committed to sustainable practices and share similar values.
Company approached re:cinq after attending a talk about optimising server utilisation at KubeCon in Paris. They recognized the potential for environmental benefits and wanted to improve their setup.
How we did this
Our methodology is rooted in the research we are doing to reduce CO₂ emissions from IT.
We sat down with the Platform team and asked them to walk us through their system. We utilised their analytics system, which in this case was a Prometheus and Grafana setup. The agenda was defined by company, which was a great decision as they know their systems better than anyone and understand the time required to discuss each component. We had the pleasure of working through each environment, the architecture design, as well as the CI/CD pipeline thus, providing opportunities to clarify decisions that were made, as well as understand the key value that each component brings.
As we went through each component, we could see the signs of a start-up moving into a scale-up:
- Startup: do everything as quickly as possible. Try to maintain quality and maintainability, but adding value is the higher priority. In essence, the short-term picture of survival.
- Scaleup: maintain delivering value, but start focusing on the longer term picture, asking how to scale what has been built, and maintain previous value so that less time is spent fixing the past.
In essence, a startup is how you make money, and a scaleup is how you keep making money.
Observations and Recommendations
The goal of the assessment was to see where we could reduce emissions without impacting efficacy. Our observations included:
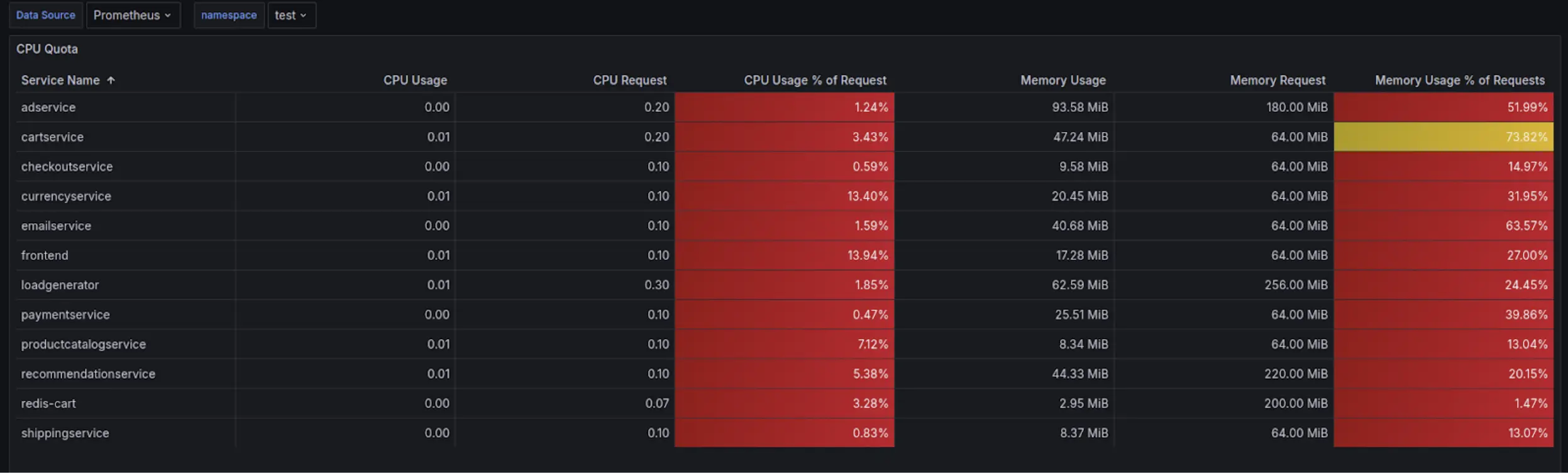
Properly provision workloads
Many companies over-provision resources. We helped engineers by building dashboards that showed the right resource requests, reducing waste while maintaining reliability.
Work better with Kubernetes Autoscaling
Properly calculating resource requests improved autoscaling responsiveness and reduced unnecessary emissions.
Isolate scheduled workloads
By moving time-sensitive workloads to dedicated resources, idle consumption was avoided while enabling predictable workloads to run more efficiently.
Provide visibility to engineers
Simple dashboards empowered engineers to optimise resources themselves, shortening feedback loops and enabling better decision-making.
Bin packing
Analysing workloads allowed us to fit more onto fewer nodes, reducing unnecessary infrastructure. For example, CPU-heavy workloads were placed on CPU-optimised nodes.
Testing environments
Idle testing environments were scaled down during weekends and off-hours, cutting emissions without slowing development.
Conclusion
By applying these practices, the client reduced IT emissions from 967.59 kgCO₂eq/month down to 580.55 kgCO₂eq/month.
That’s equivalent to driving a petrol car 1590 KM less per month — concrete sustainability gains without compromising performance.
Footnotes
- All numbers are rough estimates based on information provided by the client and Teads dataset, actual emissions may vary.
